Bed bugs are a persistent pest that can quickly infest homes and businesses. Understanding their life cycle is crucial for effective management. One key aspect is their lifespan. But what is the life expectancy of a bed bug?
In this article, we will explore the typical life expectancy of bed bugs and examine factors that influence their longevity, from environmental conditions to feeding habits.
We’ll also trace the stages from egg to adult and uncover what determines how long they survive. Let’s start!
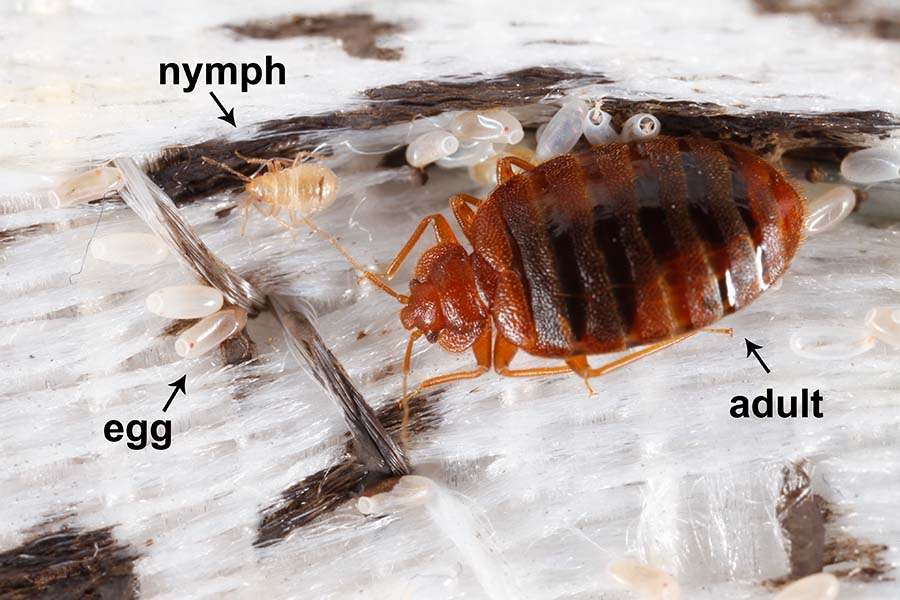

What Is the Life Expectancy of a Bed Bug Across Different Stages?
Bed bug eggs hatch in 6-10 days, with faster hatching at higher temperatures. When undisturbed, eggs have high survival rates but are vulnerable to desiccation and extreme temperatures.
Proper conditions are crucial for egg viability. But do bed bugs have larvae? No. Eggs transform into adults through the five nymphal stages, each lasting about a week. They can live months without feeding, but regular blood meals are needed to mature. And factors like temperature and host access affect nymph longevity.
So, how long can one bed bug live? Under ideal conditions, adult bed bugs can live for 12 to 18 months, but regular blood meals are essential for survival.
Additionally, temperature, humidity, and access to hosts impact their lifespan, with starvation significantly reducing it. Female bed bugs generally outlive males due to their egg-laying responsibilities.
Factors Influencing Bed Bug Longevity
Environmental conditions are critical for bed bug survival. Warm temperatures and moderate to high humidity support their longevity, while extreme temperatures and low humidity can shorten it. Having secure, undisturbed harborages is also essential for their well-being.
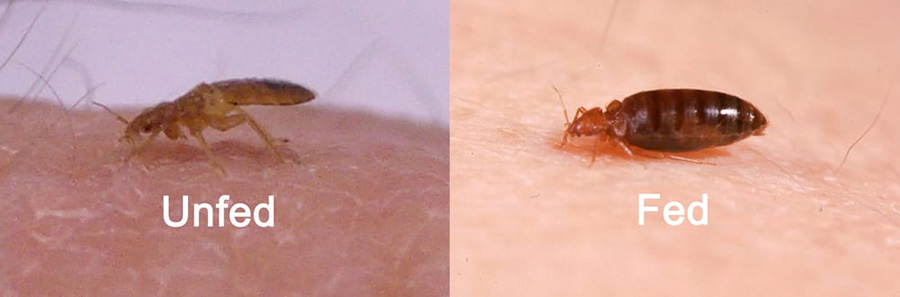
Furthermore, regular access to blood meals is vital for their survival and longevity. Frequent feedings on available hosts can extend their lifespan, but prolonged starvation dramatically reduces it. The nutritional quality of the blood they consume also impacts their health and vitality.
Moreover, reproductive activities, such as egg-laying and mating, are energy-intensive and can shorten the lifespan of female and adult bed bugs. Plus, the demands of rearing offspring can decrease the mother’s longevity.
Lifespan in Different Environments
Bed bugs thrive in warm, humid conditions between 70-80 °F and 50-70% humidity, allowing them to reach maximum lifespan. But extremes aren’t their friends; anything hotter than 113 °F or colder than 32 °F spells disaster, and low humidity leads to desiccation.
Home environments often provide stable, suitable conditions for bed bugs to fully thrive. In contrast, variable temperatures, humidity, and host availability in commercial settings like hotels can shorten their lifespan.
Various factors, such as clutter, the effort put into treatment, and levels of disturbance, also influence longevity. Environments that are more challenging to control tend to sustain populations for longer periods.
Effects of Feeding Frequency
Bed bug feeding frequency directly impacts their reproductive output and longevity. Regular blood meals are essential for their reproductive success, as blood provides vital nutrients needed for egg production and development. So, bed bugs that feed regularly have higher reproductive rates, laying more eggs than those with irregular feeding patterns.
Moreover, consistent feeding extends bed bugs’ lifespans. Access to frequent blood meals ensures their survival over extended periods, allowing them to thrive and reproduce in favorable conditions. This ability to survive longer periods between meals enhances their resilience and ability to establish persistent infestations in human environments.
Conclusion
What is the life expectancy of a bed bug? Bed bugs can live for 12 to 18 months under optimal conditions, but their lifespan is heavily influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and access to hosts.
Regular blood meals are essential for their survival and reproductive success, with frequent feeding significantly extending their lifespan. This resilience allows bed bugs to persist in human environments, making control efforts challenging.
With this insight, you can now make more informed decisions about treatment and prevention techniques. We hope this article helped you better understand bed bug life expectancy and how to apply that knowledge to your pest management efforts.
